Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Muramatsu, Kazuhiro; Sai, Kazunori*
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-017, 101 Pages, 2002/08
A visualization system on the Earth Simulator is developped. The system enables users to see a graphic representation of simulation results on a client terminal simultaneously with them being computed on the Earth Simulator. Moreover, the system makes it possible to change parameters of the calculation and its visualization in the middle of calculation. The graphical user interface of the system is constructed on a Java applet. Consequently, the client only needs a web browser, so it is independent of operating systems. The system consists of a server function, post-processing function and client function. This report describes mainly the usage of the server and post-processing functions.
Yokokawa, Mitsuo; Saito, Minoru*; Ishihara, Takashi*; Kaneda, Yukio*
Hai Pafomansu Komputingu To Keisan Kagaku Shimpojium (HPCS2002) Rombunshu, p.125 - 131, 2002/01
With the advent of supercomputers, large-scale direct numerical simulations(DNS) of the Navier-Stokes equations are possible to carry out. However, larger scale DNS is required to make turbulence clear and to make a parameterization of turbulence. The Earth Simulator is a distributed memory parallel supercomputer whose peak speed is 40 Tflop/s and it is very useful to make a very large-scale DNS. Simulation codes named 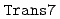 have been developed for the Earth Simulator and their correctness have been validated by compareing the simulation results by
have been developed for the Earth Simulator and their correctness have been validated by compareing the simulation results by 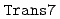 with ones by a conventinal code. The sustatined performance of 3.72Gflop/s is obtained in the execution of the serial version with the problem size of
with ones by a conventinal code. The sustatined performance of 3.72Gflop/s is obtained in the execution of the serial version with the problem size of 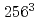 on an arithmetic processor(AP) of the Earth Simulator. Speedup of about 7 is achieved in 8APs by the parallelized code. Sppedup is degraded by the execution of 8 processor nodes, however, efficiency of 25% against the peak performance is obtained for the problem size of
on an arithmetic processor(AP) of the Earth Simulator. Speedup of about 7 is achieved in 8APs by the parallelized code. Sppedup is degraded by the execution of 8 processor nodes, however, efficiency of 25% against the peak performance is obtained for the problem size of 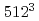 .
.
Yokokawa, Mitsuo; Saito, Minoru*; Hagiwara, Takashi*; Isobe, Yoko*; Jinguji, Satoshi*
Nihon Keisan Kogakkai Rombunshu, 4, p.31 - 36, 2002/00
Earth simulator is a distributed memory parallel system which consists of 640 processor nodes connected by a full crossbar network. Each processor node is a shared memory system which is composed of eight vector processors. The total peak performance and main memory capacity are 40Tflops and 10TB, respectively. A performance prediction system GS for the Earth Simulator has been developed to estimate sustained performance of programs. To validate accuracy of vector performance prediction by the GS
for the Earth Simulator has been developed to estimate sustained performance of programs. To validate accuracy of vector performance prediction by the GS , the processing times for three groups of kernel loops estimated by the GS
, the processing times for three groups of kernel loops estimated by the GS are compared with the ones measured on SX-4. It is found that the absolute relative errors of the processing time are 0.89%,1.42% and 6.81% in average for three groups. The sustained performance of three groups on a processor of the Earth Simulator have been estimated by the GS
are compared with the ones measured on SX-4. It is found that the absolute relative errors of the processing time are 0.89%,1.42% and 6.81% in average for three groups. The sustained performance of three groups on a processor of the Earth Simulator have been estimated by the GS and those performance are 5.94Gflops,3.76Gflops and 2.17Gflops in average.
and those performance are 5.94Gflops,3.76Gflops and 2.17Gflops in average.
Uehara, Hitoshi
JAERI-Data/Code 2001-010, 41 Pages, 2001/03
Distributed parallel simulation software with message passing interfaces has been developed to realize large-scale and high performance numerical simulations. The most popular API for message communication is an MPI. The MPI will be provided on the Earth Simulator. It is known that performance of message communication by using the MPI libraries gives a significant influence to a whole performance of simulation programs. We developed an MPI benchmark program library named MBL in order to measure the performance of message communication precisely. The MBL measures the performance of major MPI functions such as point-to-point communications and collective communications and the performance of major communication patterns which are often found out in conventional applications. In this report, the description of the MBL and the performance analysis of the MPI/SX measured on the SX-4 are presented.
Yokokawa, Mitsuo; Tsuda, Yoshinori*; Saito, Minoru*; Suehiro, Kenji*
Proceedings of 4th Annual HPF User Group Meeting (HUG2000), p.124 - 130, 2000/00
no abstracts in English